Image by jcomp on Freepik
With the ever-increasing demand for sustainable and efficient agricultural practices, researchers and gardeners are always exploring innovative methods to boost crop yields and minimize environmental impact.
Electroculture has a history dating back to early experiments in the 18th century, and there are ongoing discussions and research on its potential applications and effectiveness.
While some gardeners and enthusiasts claim positive results with electroculture, it is always advisable to approach these techniques with an open mind and evaluate their efficiency based on personal experience.
Table of Contents
What is Electroculture Gardening
Electroculture gardening, also known as electroculture or electrogardening, is a method that utilizes electricity to stimulate healthy plant growth.
It can involve different modes of application:
- Running a low electrical current through plants, water, or soil
- Creating an electromagnetic field around the plants using copper antennas
- Harnessing atmospheric electricity with copper wires to enhance plant growth
In this article, we will explore the latter. Meaning the copper wires.
Copper is commonly used in electroculture to transmit and harness electrical energy for the benefit of plants. By using copper wire or magnets, electroculture gardening enthusiasts claim that plant growth can be boosted by 100% to 200%. The wire acts as a conduit for atmospheric electricity, which is believed to deliver essential nutrients to the soil and stimulate plant growth.
If you would like a more broad approach we wrote about revolutionizing agriculture with electrical technology check it out.
This article includes affiliate links, meaning we will earn a small commission if you decide to purchase any of the affiliated items.
How to Promote Electroculture in Your Garden
Electroculture with areal copper antennas involves strategically placing these in your garden to create electromagnetic fields that positively impact plant growth.
- Start with a Small Area: Begin by implementing electroculture gardening in a small section of your garden. This allows you to observe and compare the growth and health of plants in the treated area with the rest of your garden.
- Create an Antenna: Copper wire antennas are commonly used in electroculture. You can make antennas in the form of pyramids, coils, or simple wire structures. Ensure that your antenna is properly grounded.
- Placement of the Antenna: Position the antenna near the plants you want to promote growth in. Ideally, the antenna should be placed near the plant’s root zone.
- Monitor Plant Growth: Observe the plants in the treated area and compare their growth, yield, and overall health with the rest of your garden. Document your observations and make note of any differences or improvements.
- Experiment and Adjust: Electroculture gardening techniques can vary depending on plant species, soil conditions, and climate. Experiment with different antenna designs, and placements, to find what works best for your specific garden.
- Share Your Experience: If you find success with electroculture gardening, consider sharing your experiences with fellow gardeners, local gardening communities, or online platforms. This helps raise awareness about electroculture and encourages others to explore this gardening technique.
If you’re more of a book worm check out ELECTROCULTURE FOR BEGINNERS – A lovely paperback by Errol Ramos.

Types of Antennas in Electroculture Gardening
While wrapping plants in copper may seem like a convenient alternative, don’t do it. Create a simple antenna and place it near the plants insert it approximately 6-8 inches into the soil.
Or if you want to be more extravagant about it there are more ways to create antennas.
Try it Gardening on Pinterest
- Spiral antenna: A copper wire inserted into the ground, that can be wrapped around a piece of wood or twisted into a spiral around another thicker wire. If you’re more of a fancy type you can even buy a Fibonacci Coil Winding Jig.
Or just browse it here.
Fibonacci Coil Winding Jig for Electroculture Gardening
To make things even easier you can opt for pre-made plant stakes like these.
| Electroculture Yield Growth Booster for Rapid Plant Growth (5 Pack) Material Wood, Copper Color Beige Brand Dealzer Item Dimensions: 15 x 1.5 x 1 inches | |
| Electroculture Plant Stakes (6 Pack) Small 6 Pack 11.5 inches Material: Wood, Copper Brand: GUSUCIN Dimensions: 12 x 1.18 x 1.18 inches |
This method maximizes the exposure of the plant’s roots to the electrical charges present in the atmosphere.
- Grounding copper wire: The most common method involves burying a copper wire in the soil and connecting it to a grounded metal rod or stake. The copper wire acts as a conductor, allowing atmospheric electricity to flow into the earth and reach the plant’s roots.

Soft Copper Wire, 16 Gauge, 126 Feet, 1 Pound Spool
You can browse copper wires here.
- Copper pyramid: This can be used for seed germination. These pyramids are often built following the golden ratio and are believed to possess remarkable powers that facilitate plant growth, production, and resilience.
- Copper wire mesh: Using a copper wire mesh laid on the soil surface creates an electric field that envelops the plants, providing a continuous supply of atmospheric electricity.
Copper Mesh – 5 Inches x 30 ft
Browse more here.
- Copper wire trellis: If you have climbing plants or vines, consider using a copper wire trellis. As the plants grow and intertwine with the trellis, they come into contact with the copper wire, benefiting from the electrical stimulation.
- Electrified watering system: An innovative approach involves incorporating copper wire within a watering system. As the water passes through the wire, it becomes charged with atmospheric electricity, providing a direct boost to the plant’s roots during irrigation.
Magnets can also help in speeding up the germination process and can be linked with galvanized wire to form subterranean magnetic antennas oriented from South to North.
Benefits of Applying Atmospheric Electricity with Copper Wire
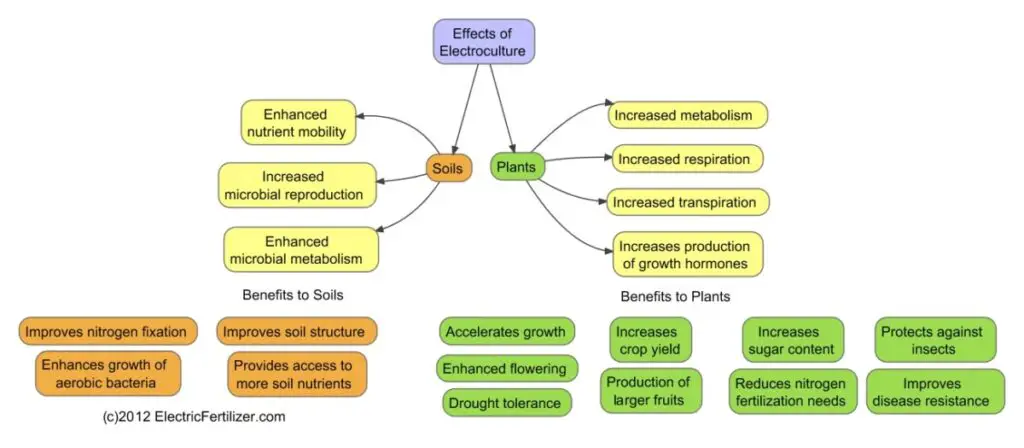
Benefits of Electroculture
Implementing electroculture gardening techniques can offer several benefits that contribute to the overall health and productivity of your plants, including:
- Accelerated growth: The electrical stimulation provided by copper wire encourages plants to grow at an accelerated rate, resulting in faster and healthier development.
- Improved nutrient uptake: The enhanced electrical activity in the soil facilitates the absorption of essential nutrients by the plant’s roots, leading to improved overall health and vigor.
- Strengthened immunity: The electrical charges conveyed through copper wire bolster the plants’ immune system, making them more resistant to diseases, pests, and adverse environmental conditions.
- Pest repellent: The copper wire creates an electric charge around plants or in the soil. This charge can deter pests like slugs and snails from feeding on the plants
- Enhanced flowering and fruiting: Atmospheric electricity promotes the production of flowers and fruits, leading to a bountiful harvest and vibrant blooms in your garden.
- Sustainable and eco-friendly: This technique harnesses the power of nature without relying on harmful chemicals or synthetic additives, making it an environmentally friendly approach to plant cultivation.
Plants that Show the Best Results with Electroculture

The effectiveness of electroculture gardening can vary depending on factors such as plant type, environmental conditions, and individual preferences. However, certain plants are often mentioned in the context of electroculture due to their potential positive response to the technique. Here are a few examples:
- Tomatoes are commonly cited as a plant that benefits from electroculture. Some gardeners claim that electroculture can enhance tomato growth, yield, and flavor.
- Peppers, including bell peppers and chili peppers, record increased fruit production and improved flavor.
- Plants like lettuce, spinach, and kale are good candidates for electroculture. The technique may help promote healthy leaf growth and improve overall plant vigor.
- Various herbs, like basil, parsley, and cilantro, can display enhanced flavor and stimulated growth.
- Some gardeners are experimenting with electroculture techniques on fruit trees, such as citrus trees or apple trees. They claim that electroculture can potentially increase fruit production and improve fruit quality.
The response to electroculture gardening can vary among individual plants, and the effects may not be the same for every gardener or garden. The best approach is to experiment with different plant species in your garden and observe the results.
The Role of Copper in Plant Growth
Copper plays an important role in the growth and development of plants. It functions as an essential mineral nutrient and is involved in various morphological, physiological, and biochemical processes. Copper acts as a cofactor in several enzymes, performing essential roles in:
- Photosynthesis
- Respiration
- Electron transport chain
- Cell wall metabolism
- Oxidative stress protection
- Biogenesis of molybdenum cofactor
- Defense genes
Copper is also necessary for the synthesis of lignin and is involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates and proteins in plants.
Copper deficiency can have severe effects on plant growth and productivity. Symptoms of copper deficiency typically appear in the newer leaves, leading to cupping, chlorosis (yellowing), and necrotic spots, particularly on the leaf margins.
High levels of copper in the growing medium can hinder root growth and compete with the uptake of other essential nutrients such as iron, molybdenum, or zinc.
Maintaining an appropriate balance of copper is important for optimal plant growth.
There are other methods to improve plant growth like Regenerative Agriculture. Which focuses on restoring the general health of the soil, and mimicking natural habitats.
Copper Gardening Tools vs Iron Gardening Tools
Copper and iron are both materials that are commonly used for gardening tools.
Copper is a soft and malleable metal that is resistant to corrosion. This makes it a good choice as it can withstand exposure to moisture and soil. It also has antimicrobial properties, which means it can help to prevent the growth of bacteria and fungi on gardening tools. This can be particularly useful for tools that come into contact with plants that are susceptible to diseases.
Here are some Amazon bestsellers.
| Esschert Design GT119 Copper-Plated Mini Tools Brand: Esschert DesignColor: Brown Material: CopperItem Dimensions: 0.91 x 1.34 x 7.28 inches | |
| Esschert Design GT119 Copper-Plated Mini Tools Brand: Esschert DesignColor: Brown Material: CopperItem Dimensions: 0.91 x 1.34 x 7.28 inches | |
| Esschert Design GT117 Copper-Plated Rake Fork Material: Copper Color: Copper Brand: Esschert Design Dimensions: 1.69 x 2.95 x 11.14 inches Handle Material: Wood | |
| Esschert Design GT121 Copper-Plated Dibber Material: Copper Color: Copper Brand: Esschert Design Handle Material: Wood | |
| Esschert Design GT124 Copper-Plated Pruner Material: Copper Color: Copper Brand: Esschert Design Dimensions: 0.83 x 2.44 x 8.07 inches Handle Material: Wood | |
| Esschert Design GT120 Copper-Plated Rake Fork Material: Copper Color: Copper Brand: Esschert DesignItem Dimensions: 2.36 x 4.45 x 14.65 inchesHandle Material: Wood |
Iron, on the other hand, is a harder and more durable metal than copper. It is less likely to bend or break under heavy use, and it can be sharpened to a very fine edge, making it ideal for cutting and pruning tasks. However, iron is prone to rusting, which can be a problem if it is not properly cared for.
If you are looking for tools that will resist corrosion and help prevent the spread of disease, copper may be a better choice.
FAQs
- Can I simply use a copper pipe instead of constructing an antenna?
While you can certainly use a copper pipe, it is worth noting that copper coils tend to yield better results. Copper coils effectively harness the flow of energy.
- Instead of making an electroculture antenna, can I just wrap my plants in copper?
Wrapping plants in copper is not recommended, not all plants appreciate being entangled.
- Does electroculture work on indoor or potted plants?
Electroculture works remarkably well on indoor plants! You can create a simple indoor antenna using something as basic as a chopstick.
- What should be the height of the electroculture gardening antenna?
You have the freedom to make your atmospheric antennas as tall as you desire. On average, antennas measuring 6 feet or more are ideal for gathering greater atmospheric energy.
- How much area does an electroculture antenna cover?
Typically, a single 6-foot antenna can cover approximately 225 square feet.
- Where can I find copper wire for electroculture?
You can find copper wire at Home Depot, Lowes, Ace Hardware, or Menards.
- Does the thickness of the copper matter for electroculture?
For electroculture gardening, any thickness of copper wiring will work, although heavier gauges may provide better conductivity


